
Type and hit enter

A specialized field within internal medicine, focuses on diagnosing and treating kidney problems.
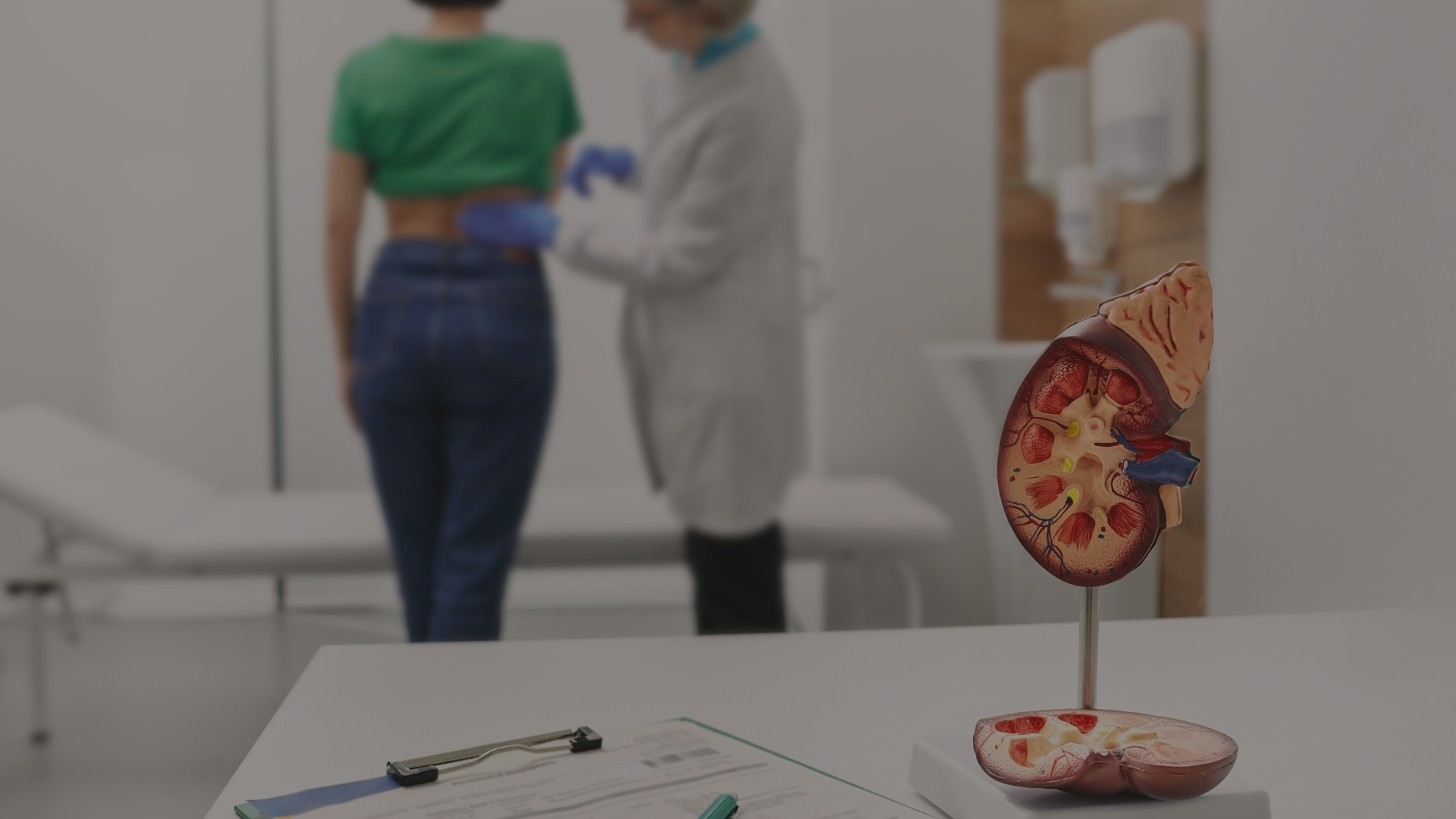
Nephrologists play a crucial role in managing infections, neoplasms, and abnormalities of the kidney, collecting system.
To assess kidney damage and disorders, various measures are employed, including:
Physical Examination:
Common symptoms like edema (swelling of legs and face) are indicative of fluid imbalance associated with kidney disease.
Anemia, often a consequence of long-term renal dysfunction, may be observed.
High blood pressure, frequently coexisting with kidney disease, is monitored.
Blood Tests:
Levels of urea, creatinine, and electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphates, and blood urea nitrogen) are evaluated for abnormalities.
Blood tests may also screen for pathogens such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, AIDS, and antibodies indicating conditions like lupus, amyloidosis, or multiple myeloma.
Urine Analysis:
Detection of excess proteins in urine, particularly common in diabetic nephropathy and chronic kidney disease.
24-hour urine samples assess total protein excretion, indicating renal failure.
Microscopic examination identifies cells, casts, and structures related to kidney and urinary tract health.
Ultrasound Scanning:
Identifies conditions like kidney stones, hydronephrosis, and polycystic kidney disease.
MR Angiography:
Precise imaging of blood vessels within the kidneys to identify irregularities.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR):
Assesses kidney function by measuring the clearance of substances.
These comprehensive measures aid in diagnosing and understanding various kidney-related issues, allowing for targeted and effective treatment. Regular monitoring and diagnostic assessments contribute to better management of kidney health and overall well-being.
Our Nephrology Department is a leading provider of exceptional clinical care for individuals facing acute and chronic kidney diseases. Situated in India and boasting cutting-edge technology, our program is dedicated to addressing a wide spectrum of kidney conditions, including clinical nephrology, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and renal transplantation.
Our team of highly skilled doctors is renowned for their clinical expertise, catering to patients of all ages, from children to adults. With a focus on delivering comprehensive care, we have a team of kidney transplant experts, nephrologists, and support staff equipped with the technological know-how to tackle challenges associated with life-saving procedures.
We pride ourselves on offering advanced diagnostics, thorough pre-operative evaluations, dialysis support, state-of-the-art surgical facilities, and meticulous post-operative care to minimize infection risks. Our dialysis services, managed by a skilled team of nephrologists, nurses, and certified hemodialysis technicians, ensure top-notch care for patients with kidney disorders.
Recognizing the unique needs of our patients, we are committed to providing high-quality care, instilling hope, and offering guidance. The satisfaction and comfort of our patients remain paramount throughout our services. Trust us for a dedicated and advanced approach to kidney care, ensuring successful outcomes for those we serve.
Nephrology departments offer a range of specialized services for the treatment of kidney diseases and pathology, catering to diverse patient needs. Some key services include:
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT):
CRRT is employed for critically ill patients with high metabolic rates.
It involves the gentle removal of waste and excess fluids without causing hypotension.
Blood is circulated through a hemofilter in a slow hemodialysis process.
Peritoneal Dialysis (CPD):
During peritoneal dialysis, dialysate is introduced into the abdominal cavity via a catheter.
The dialysate remains in the cavity for several hours, allowing the removal of waste materials through capillaries.
Subsequently, the dialysate is drained.
Plasma Dialysis (Plasmapheresis):
Plasmapheresis is a therapeutic procedure that separates plasma from blood, removing harmful substances.
This process is particularly useful in addressing certain autoimmune conditions and kidney-related pathologies.
Liver Dialysis (MARS Therapy):
MARS therapy, based on albumin dialysis, effectively eliminates protein-bound and water-soluble toxins.
It may contribute to liver regeneration and stabilization of key organ functions.
Kidney Transplant:
Kidney transplantation involves surgically replacing a diseased kidney with a healthy one from a living or deceased donor.
This procedure offers a long-term solution for end-stage renal disease.
Combined Kidney & Liver Transplant and Kidney Biopsy:
Some nephrology departments offer combined kidney and liver transplants for patients with dual organ needs.
Kidney biopsy, a diagnostic procedure, may also be performed to assess kidney tissue for pathology.
Each service is tailored to address specific conditions, providing patients with comprehensive and specialized care. These interventions aim to enhance overall kidney health, improve organ function, and contribute to the well-being of individuals with kidney-related disorders.

Feel free to contact us! Our expert team will be happy to assist and guide you. We are here to answer your questions and offer solutions that fit your needs.
1-100/29/9/4 and 4A Gopanapally,
Serilingampalle (M), Telangana 500046
Branch 2:
Plot No: 0-8 Sy No: 1-13, Shanthi Classic, Huda Trade, Lingampally, Hyderabad – 500019 (Near Vijetha Super Market, Beside Nallagandla Road SBI Branch)
Lingampally Branch:
H.No:2-38/A/15, Taranagar, Lingampalli, K.V, Serilingampalle (M), Hyderabad, Telangana 500019
support@akshahospitals.com
akshahospitals@gmail.com
+91 7402549999
+91 7402679999
© Copyright 2024. Aksha Hospitals. All Rights Reserved. | Designed by hiremystudios Australia.
Our healthcare professionals will help you determine the most convenient time and schedule an appointment that suits your needs.
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart